Facilities
Experimental Installations
A total of 10 GEOLAB partners are offering access to 11 experimental installations. To view information on facilities available for access, please click on the facility.
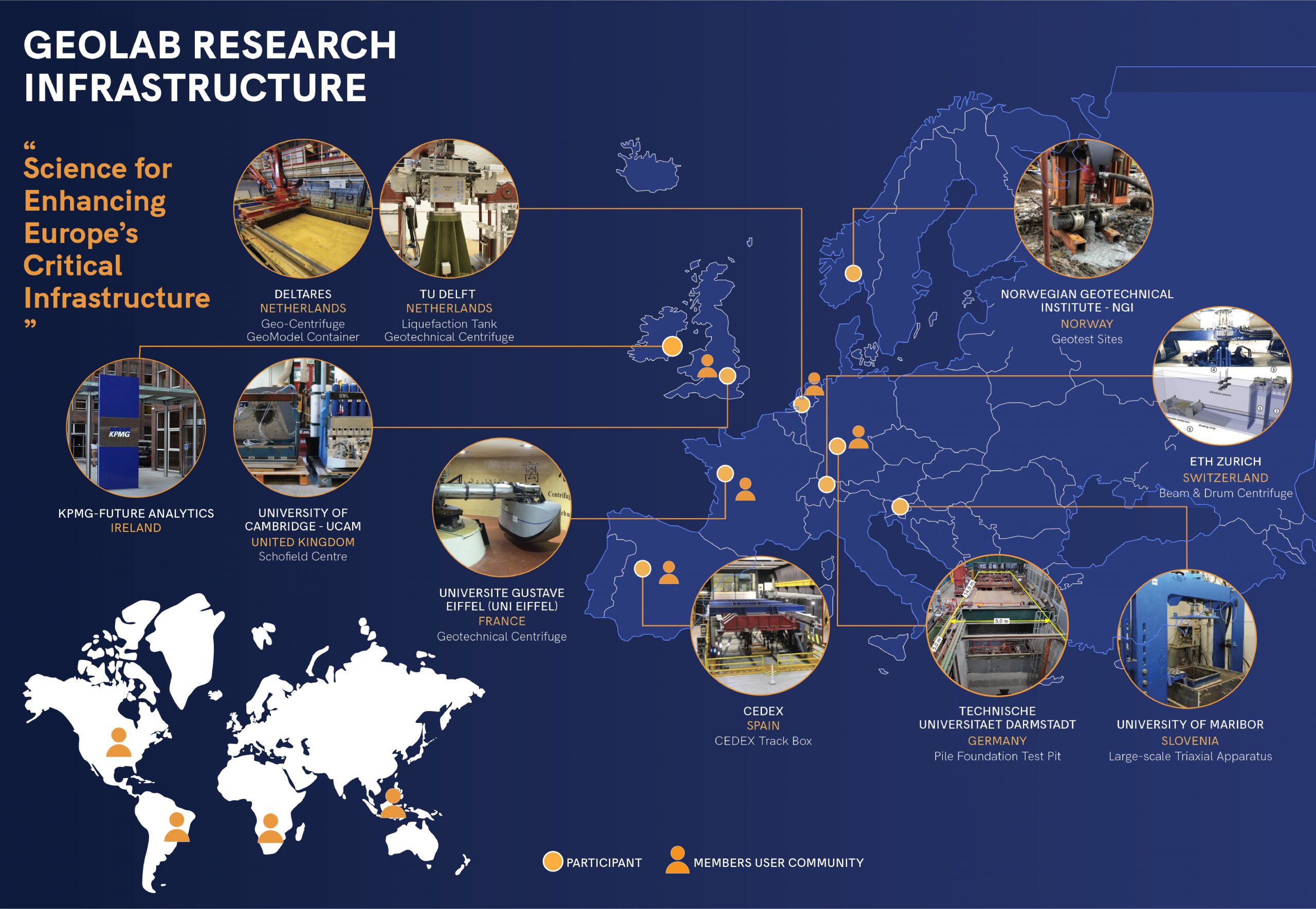
A total of 10 GEOLAB partners are offering access to 11 experimental installations. To view information on facilities available for access, please click on the facility.
